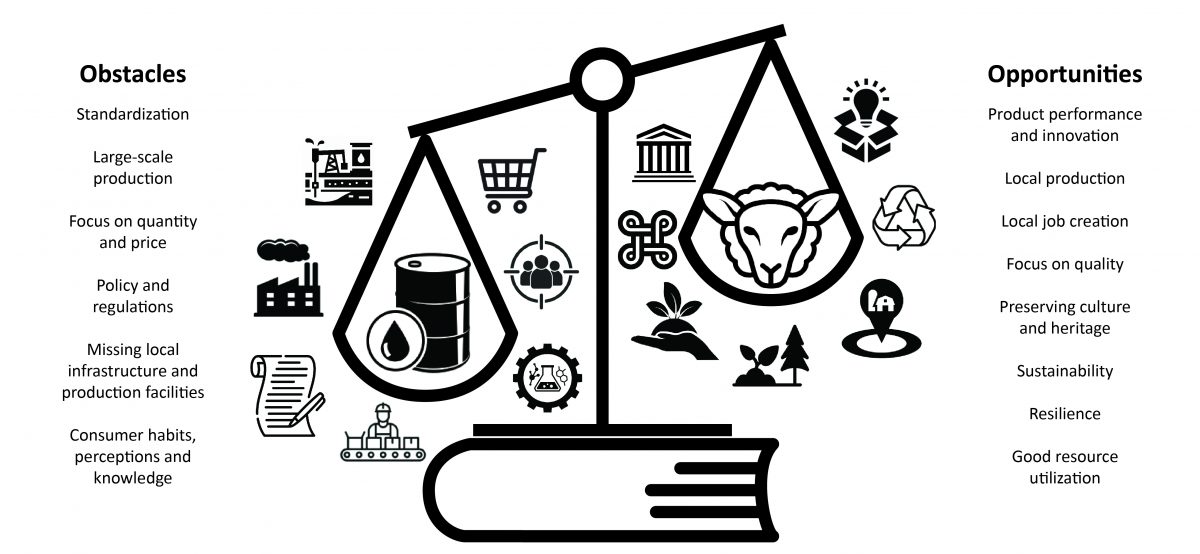
New papers accepted in international journals
Two new papers have been accepted by international journals relating to the WOOLUME project, one on the biodegradation of wool fibers and one on the acoustic properties.
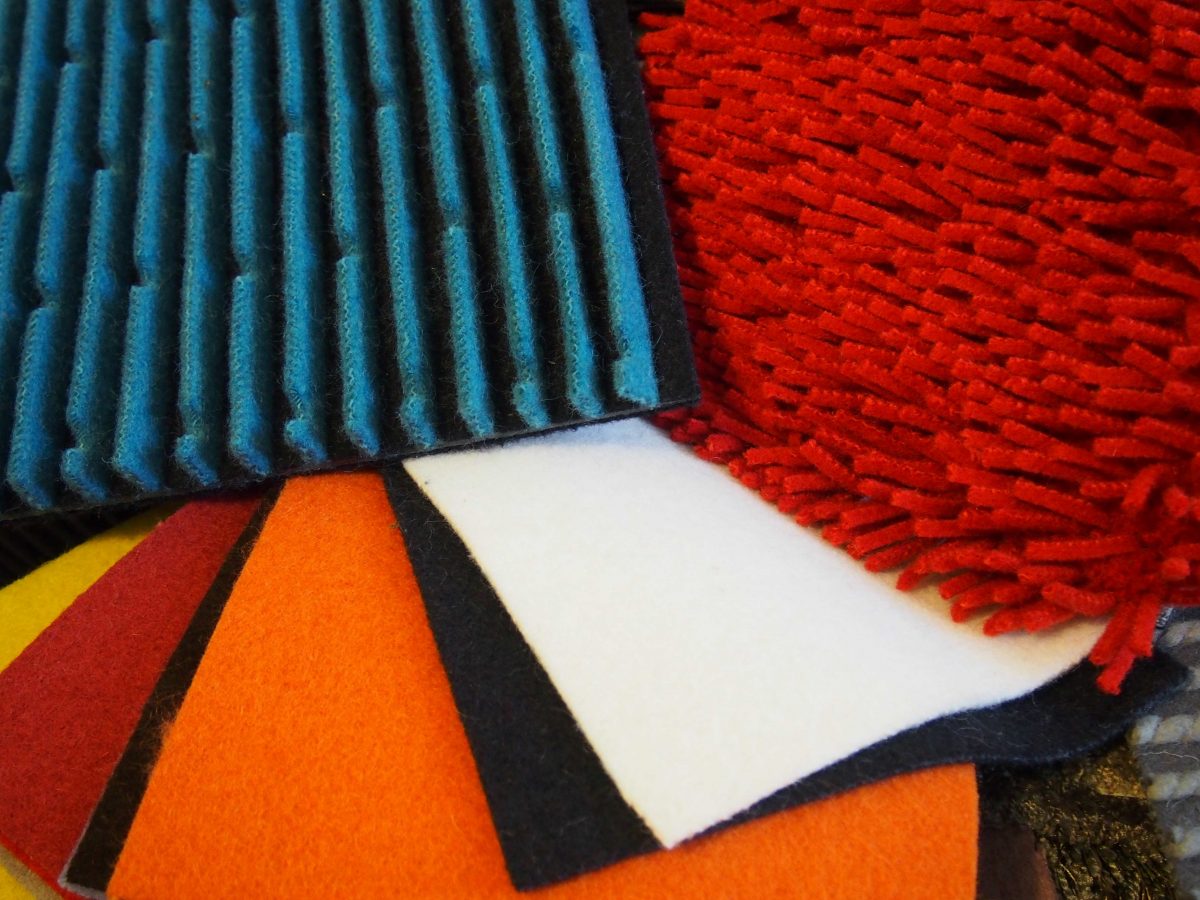
The very latest is on the acoustic properties of tufted carpets coupled with the underlayment made from tannery wool waste: Acoustic Performance of Tufted Carpets Coupled with Underlayment Produced from Tannery Wool Waste in the journal Materials. The authors are Jan Broda, Katarzyna Kobiela-Mendrek, Marcin Baczek and Monika Rom.
To better use local sources of wool, the coarse wool of mountain sheep was used to form a carpet pile layer, while the waste wool from the tannery industry was applied to form carpet underlayment. During investigations, the acoustic performance of the carpets was assessed. The carpets’ sound absorption coefficients and transmission loss were studied, and it was revealed that the adding of underlayment improves the carpet’s sound absorption only at medium sound wave frequencies.
It was concluded that wool nonwovens can be used as an effective, eco-friendly, sound-absorbing carpet underlayment, which can improve wool utilisation and contribute to the reduction in environmental pollution caused by plastic residues.
Excessive noise has become a severe and pervasive pollutant that harmfully influences physical and mental health. Exposure to domestic noise negatively affects human well-being, impairs productivity, generates higher stress, and contributes to somatic complaints. Given the adverse effects of noise, the urgent need to reduce noise levels in homes, classrooms, open-plan offices, workplaces, and public facilities is highly significant and desirable today. For many years, various textiles used as window curtains, tapestries, upholstery, wall and ceiling panels, screens, rugs, and carpets have been used to reduce noise and improve the acoustic comfort of interiors. Among these products, carpets are the most versatile, controlling indoor noise in various ways. First, carpets lower the level of noise by absorbing airborne sound. Second, they reduce the generation of floor impact sounds produced by footfalls, furniture movement, and objects dropped onto the floor. Third, carpets minimise the noise transmission through floors to adjoining rooms in multi-storied buildings.
Pile carpets, in particular, demonstrate a significant potential for noise reduction. These carpets are made of two layers that perform different functions and have different structures.

The sound absorption in the pile layer depends on the pile type (loop or cut) and its height and density. Due to the open fuzzy structure, carpets with cut piles have higher sound absorption capacity than carpets with loop piles. Increasing pile height and density increases the interphase contact surface between piles and vibrating air molecules. Then, the energy dissipated by friction is higher and the resulting sound absorption increases. The influence of other parameters characterising the pile layer, such as fibre type, yarn parameters, or knot type in knotted-pile carpets, is less distinguishable and difficult to estimate.
To access the article, click on this link.
The second of the two papers is on wool biodegradation: The Morphology of Wool Fibers Biodegraded in Natural Conditions in Soil authored by Monika Rom, Jan Broda, Tomasz Kukulski, Andrzej Gawlowski & Katarzyna Kobiela-Mendrek in the Journal of Natural Fibers.
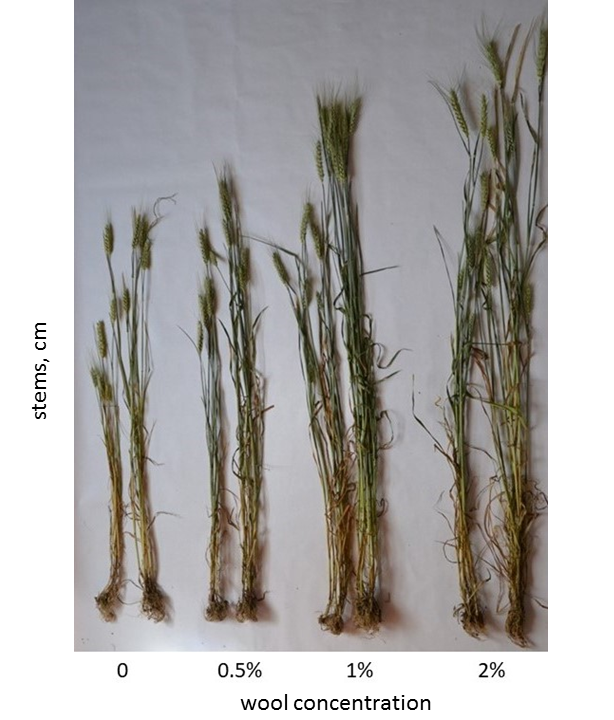
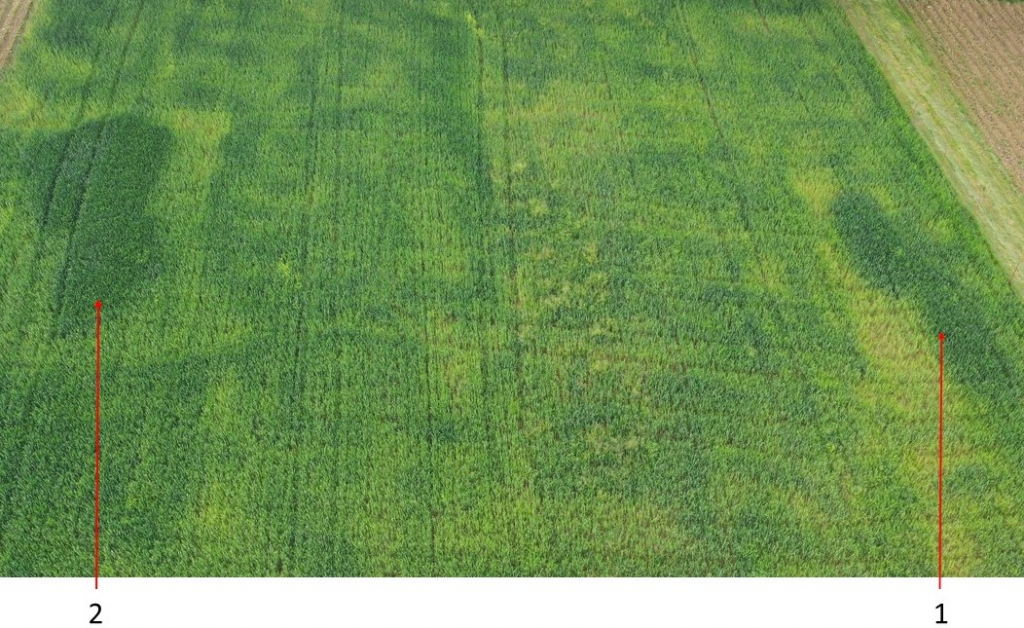
The morphology of sheep wool applied as organic fertilizer biodegraded in the soil was examined. The investigations were conducted in natural conditions for unwashed waste wool, which was rejected during sorting and then chopped into short segments and wool pellets. Different types of wool were mixed with soil and buried in experimental plots. The wool samples were periodically taken and analyzed for one year using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS). During examinations, the changes in the fibers’ morphology were observed. It was stated that cut wool and pellet are mechanically damaged, which significantly accelerates wool biodegradation and quickly destroys the whole fiber structure. On the contrary, for undamaged fibers biodegradation occurs slowly, layer by layer, in a predictable sequence. This finding has practical implications for the use of wool as an organic fertilizer, suggesting that the method of preparation can influence its biodegradation rate.
The ability of wool to support plant development in agricultural and horticultural crops has been repeatedly demonstrated. The application of wool fertilizer has led to higher yield for various vegetables and cereals. These studies have used wool of different origins and waste generated in various stages of wool processing. For instance, unprocessed and unwashed wool obtained by sheep shearing, wool sheared from animals intended for slaughter, the waste derived from scouring and carbonization, and wool recycled from shredded carpets have all been tested. In some cases, loose wool fibers were mixed with soil using agricultural machines or spread on the ground’s surface and covered with a layer of topsoil. To avoid compounding issues, the wool was cut into short segments in certain studies. In other cases, the wool was added as easily applicable pellets.
The article is available at this link.