Increasing repair of household appliances, mobile phones and clothing: Experiences from consumers and the repair industry
Kirsi Laitala, Ingun Grimstad Klepp, Vilde Haugrønning, Harald Throne-Holst & Pål Strandbakken
Abstract
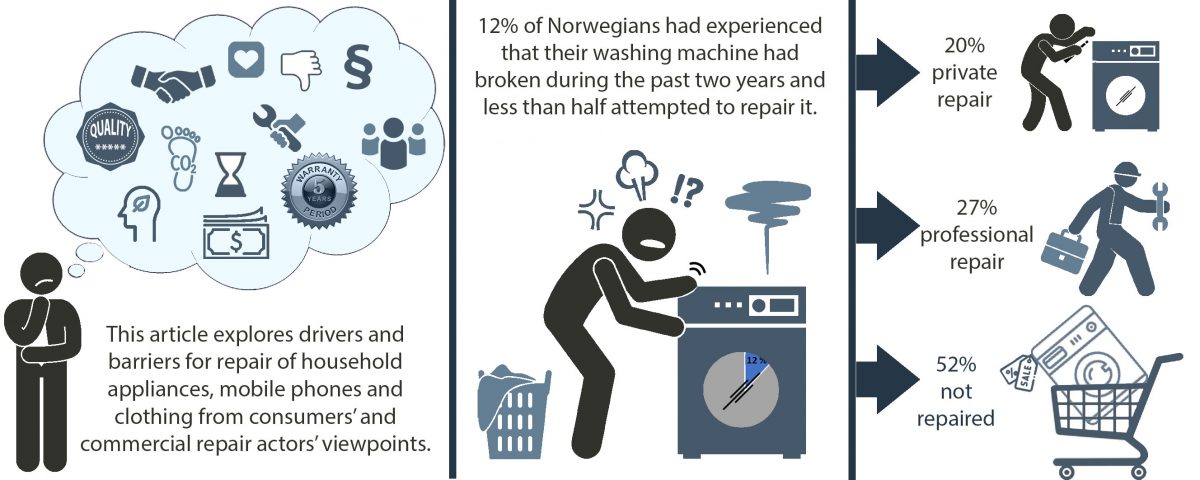
Increasing product lifespans is one of the most effective environmental strategies and therefore repair is a part of the circular economy approach that aims to keep products and materials longer in use. This article explores drivers and barriers for repair from consumers’ and commercial repair actors view-points, in order to understand how the repair rates of household appliances, mobile phones and clothing could be increased.
The study is based on a consumer survey of 1196 respondents in Norway, and 15 qualitative interviews with actors in the commercial repair industry working with repairs of household consumer goods. A surprisingly high share of repairs was conducted by consumers themselves. The main barrier is the consistently low price of new products, and often of poor quality, which contributes to low profitability in repair work for businesses and low motivation from consumers. Furthermore, access to competent personnel is a major challenge for the repair industry, a need which is expected to increase in the coming years.
Both the industry and consumers agree that better quality of products is a starting point for increased product lifespans, and this will also increase the motivation and the number of profitable repairs. These results have political implications on how to promote longer product lifespans through repair such as increased utilization and knowledge of consumers’ complaint and warranty rights.