Report from IWTO’s Round Table 2022

There seems to be renewed hope for strong wool and local production. Especially with a focus on regenerative grazing and looking at wool’s possible new (and perhaps old, but forgotten) applications.
Regenerative agriculture was a major topic at the IWTO’s Round Table in Nuremberg, Germany, and the possibility of natural fibers to make a positive contribution to climate sequestration, to biodiversity and to soil health. Heinz Zeller from Hugo Boss, said that by 2030, all natural fibers the fashion brand uses must either be from regenerative agriculture or recycled sources. UK-based Merino farmer Lesley Prior, who is helping to establish a Merino breed in several European countries with sheep that can withstand a varied climate, also spoke a lot about the theme. Prior has worked for many years with small brands in the UK, such as Finisterre. “In England they have very strict rules about what you have to report and measure,” she explained, impressing everyone with her knowledge and passion. “Remember your woolen clothes are carbon stocks,” said Prior, to eager applause.
For Polish and Norwegian wool, two lectures were of great interest. Andy Caughey, head of Wool Impact in New Zealand, aims to make “strong wool” – i.e. the same wool as Norwegian crossbred wool – “great again”. “Stop looking at the floor,” he said, referring in particular to the wall-to-wall carpets. It is all about finding new and better applications for this wool, alongside carpets and knitting yarns. Wool winter boots are an emerging market, following the footsteps of Allbirds, Kastel and many others. The new company, Wool Impact, is funded by the New Zealand government, and among the examples Caughey showed were wool band-aids (which are biodegradable), sound-absorbing panels, face masks, air filters and nappies and sanitary pads, all in wool and potentially biodegradable if disposed of in the right manner.
New Zealand, unlike Norway, does not have wool subsidies, so the cost of shearing the crossbred sheep is today higher than what the farmer receives for the wool. In connection with the use of wool in wall panels for sound absorption, a company in New Zealand had developed an additive based on a food supplement, to ensure their flame retardancy. Strict requirements for a material that is naturally flame retardant has been a headache for many, including those who supply woolen products to the military, fire brigades, police and aerospace.
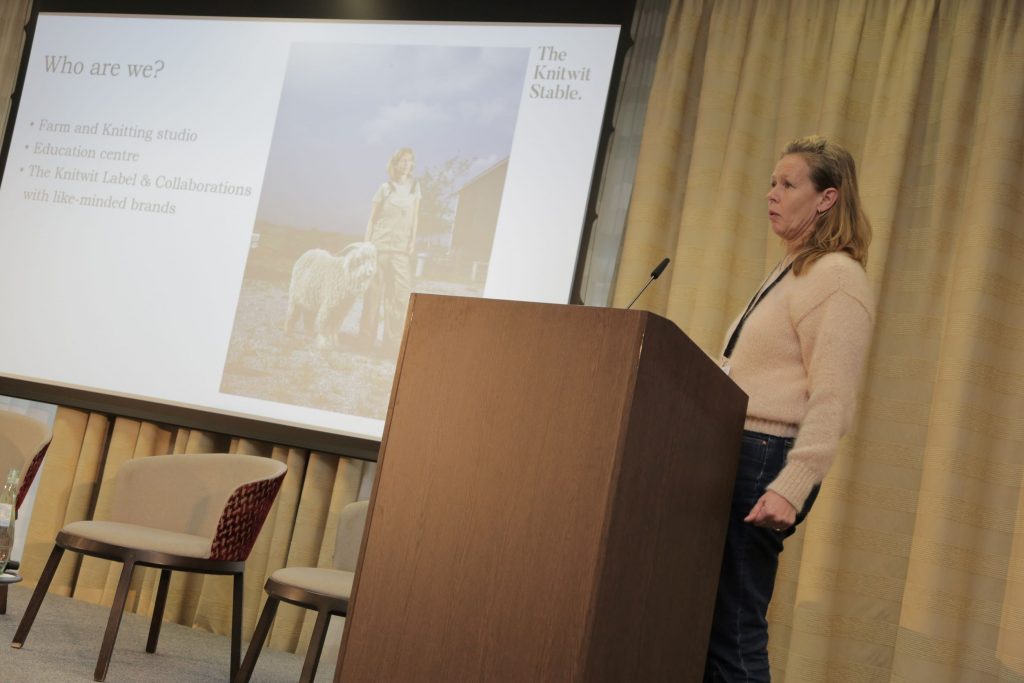

Reina Ovinge, from Holland, talked about her local wool project in Holland, The Knitwit Stable. She had worked in the fashion industry for many years, but got tired of the pressure on prices and the constant call for new collections. Although she only has 35 sheep and 35 goats, her work arouses great interest, also among EU bureaucrats, who have visited her set-up. The EU also has agreed to fund a knitting-machine, so that she can now produce clothing and other items on demand. This has led to capsule collection cooperation with Dutch fashion brands such as Scotch & Soda and Humanoid, small collections that command high prices. She has visited both Hillesvåg and Telespinn, she said, for inspiration.
We also heard about French wool (Roquefort cheese would not have had a place on shop shelves without sheep) which is mostly thrown away. France is very much struggling with the lack of a value chain for wool. We also heard about a new grazing project in the USA where the sheep graze in conjunction with solar panels, because the grass under these would otherwise have had to be cut by machines. Here, too, the topic was carbon capture, which Lesley Prior also repeated several times. She believes (but has no proof as of yet) that she is at least carbon neutral on her Tellenby Farm, perhaps even sequestering carbon. In addition, she used a reporting system called “Fair to Nature” which assesses the farm’s contribution to biodiversity every two years. And she isotope-labels the wool so that wherever it ends up, it can be traced back to her. Provenance was also something that several speakers claimed was increasingly important. In New Zealand, there is a labeling scheme that covers both the wool and the meat, New Zealand Farm Assured.
Lesley Prior had a bee in her bonnet about all that should be counted (with all the schemes and bureaucracy governing agriculture), what can be counted… and what actually counts. This is an ever-recurring discussion when it comes to regenerative agriculture, where what everyone can observe (birds chirping, bees buzzing) is probably as important as the measurement of carbon in the soil.

Whether local European wool can be used better was not a major theme during the conference, but it did resurface, and especially related to manufacturing. Nuremberg, with its famous Christmas market in the old town, is Südwolle’s hometown and therefore also the scene of the conference this time, as they were the main sponsor. Südwolle and Schneider are competitors, but at the wool congress both companies agreed that they want more production in Europe, but are struggling to recruit labor.
The topic of whether it is one of the solutions to bring down the enormous increase in production, to move production back to where consumption takes place, rather than a pessimistic belief that we will have a thriving fiber-to-fiber recycling industry in the EU, has only just begun. Interestingly enough, in light of all the arrows pointing down for the apparel industry, in light of rising prices and inflation, there was one industry that was optimistic, and that was the factory machinery manufacturers. They envision that more people than Hugo Boss will knit – and more locally – based on what is called “just-in-time” production.
Ovinge had bought herself a Stoll knitting-machine with EU funding, as mentioned, others will probably follow suit.